CSRD compliant materiality analysis
What is new?
Double materiality as starting point for sustainability reporting
As of January 1, 2024, capital market-oriented companies with more than 500 employees will be subject to the comprehensive ESG reporting requirements of the CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) for the first time. With this directive, the European Union has once again significantly tightened disclosure requirements for companies on non-financial topics. And in 2025, the group of companies subject to reporting requirements will be expanded once again, so that in the future more than 50,000 companies across Europe will have to report annually on their sustainability efforts.

But where to start with ESG reporting? The CSRD requires a materiality analysis to be carried out. Two dimensions are considered: the most important influences of the company on environmental and social issues (impact perspective) – and material risks and opportunities arising for the company from environmental and social issues (risk-and-opportunity perspective). These two perspectives of materiality analysis are also referred to as the principle of “double materiality”.
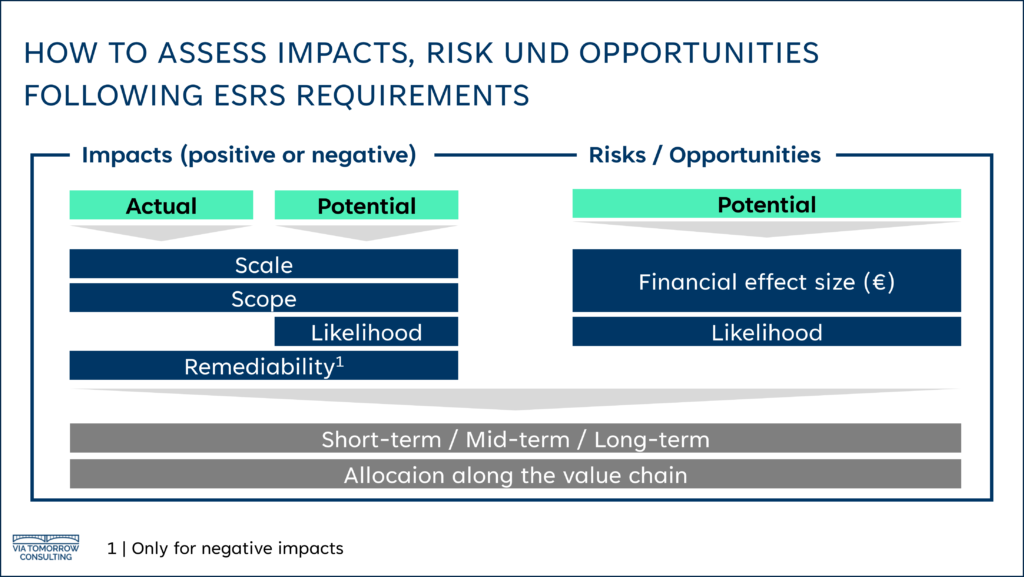
For internal and external stakeholder engagement, companies must consider all topics provided for in the ESRS (European Sustainability Reporting Standards) of the CSRD, as well as other company-specific topics. With the help of internal and external stakeholders, Impacts, Risks and Opportunities (IROs) must be assessed for each topic. The impacts are assessed using the evaluation categories “Scope,” “Scale,” “Remediability,” “Time Horizon” and – if potential impacts are involved – “Likelihood. Risks and oppportunties are assessed using the categories “Likelihood,” “Financial Effect Size,” and “Time Horizon.
In view of the complexity of the underlying ESG issues, expert assessments play a key role in these assessments. For this purpose, the ESRS provide for the consultation of both internal and external contacts (stakeholders). The latter are to be centrally involved in the inside-out perspective, as they are or could be directly or indirectly affected by possible impacts.
The assessment of all IROs provides information on which issues are material for the company. These form the cornerstone for further ESRS reporting: based on the materiality analysis, companies may delete immaterial ESG topics for their reporting, but must be all the more transparent with all material topics. This includes defining goals and action plans, creating relevant guidelines, and disclosing detailed metrics.
Materiality Analysis in the DAX-40: The Status Quo
Sustainability reporting in Germany is undergoing major changes – keyword CSRD. But how prepared are companies for the basic building block of the CSRD, the materiality analysis? Via Tomorrow looked at the current materiality analyses of all DAX40 companies to see where there are remaining gaps in their CSRD compliance.
When does materiality analysis become relevant for whom?
The CSRD has already come into force – and will apply to many companies as early as 2024. Since materiality analysis is only the first step in a series of necessary ESG tasks to fully comply with the CSRD, companies should start as early as possible.
Listed COmpanies
Last Call: For capital market-oriented companies with at least 500 employees, the new requirements will already apply from fiscal year 2024. When things start to get tight, we are the right people to contact: We will get your materiality analysis project off the ground in a structured and efficient manner - and competently over the finish line, so that you meet the requirements of the law and the reporting auditors in good time.
family businesses
Almost all companies with more than 250 employees will be subject to ESG reporting requirements from 2025. However, in many cases, non-listed companies do not yet have structured ESG reporting. To avoid being suddenly overwhelmed by the extensive requirements of the CSRD, now is the right time to take the first step with a materiality analysis - and then to develop a coherent ESG strategy and establish systematic ESG data collection.
Via Tomorrow - Your choice for a CSRD-compliant materiality analysis
Our approach to materiality analysis is characterized by exceptional efficiency, careful documentation, and the flexibility to adapt to relevant requirements such as EFRAG guideline proposals – even if they are still at the draft stage. We draw on your individual requirements and preliminary work within the company and develop a customized approach that meets the highest quality standards.
Pragmatic and efficient
With us, you will reach your goal directly: lean processes, close coordination and a focus on the relevant aspects are decisive for us when conducting a materiality analysis.

Extensively documented
We work in a clean and structured manner and adhere closely to the parameters of the ESRS. Each step is carefully recorded so that the entire materiality process stands up to the final report review.

Adaptable and fast
We know the current state of regulation and have an eye on pending changes and specifications – and are flexible to quickly adapt our approach to relevant innovations.


